publications
2024
-
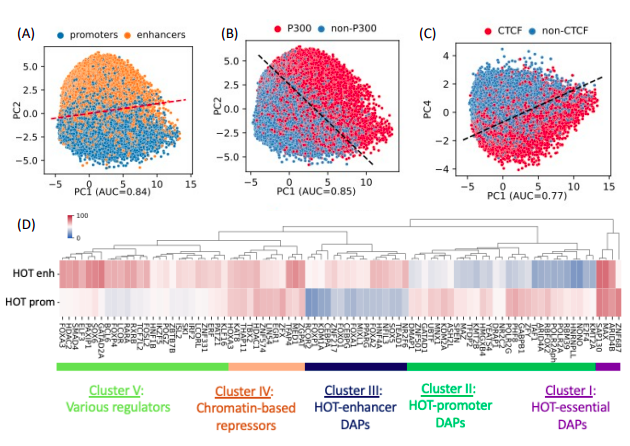 Sequence characteristics and an accurate model of high-occupancy target loci in the human genome.Sanjarbek Hudaiberdiev, and Ivan OvcharenkoeLife (in submission), 2024
Sequence characteristics and an accurate model of high-occupancy target loci in the human genome.Sanjarbek Hudaiberdiev, and Ivan OvcharenkoeLife (in submission), 2024Enhancers and promoters are classically considered to be bound by a small set of TFs in a sequence-specific manner. This assumption has come under increasing skepticism as the datasets of ChIP-seq assays of TFs have expanded. In particular, high-occupancy target (HOT) loci attract hundreds of TFs with seemingly no detectable correlation between ChIP-seq peaks and DNA-binding motif presence. Here, we used a set of 1,003 TF ChIP-seq datasets (HepG2, K562, H1) to analyze the patterns of ChIP-seq peak co-occurrence in combination with functional genomics datasets. We identified 43,891 HOT loci forming at the promoter (53%) and enhancer (47%) regions. HOT promoters regulate housekeeping genes, whereas HOT enhancers are involved in tissue-specific process regulation. HOT loci form the foundation of human super-enhancers and evolve under strong negative selection, with some of these loci being located in ultraconserved regions. Sequence-based classification analysis of HOT loci suggested that their formation is driven by the sequence features, and the density of mapped ChIP-seq peaks across TF-bound loci correlates with sequence features and the expression level of flanking genes. Based on the affinities to bind to promoters and enhancers we detected 5 distinct clusters of TFs that form the core of the HOT loci. We report an abundance of HOT loci in the human genome and a commitment of 51% of all TF ChIP-seq binding events to HOT locus formation thus challenging the classical model of enhancer activity and propose a model of HOT locus formation based on the existence of large transcriptional condensates.
@article{hudaiberdiev2023sequence, title = {Sequence characteristics and an accurate model of high-occupancy target loci in the human genome.}, author = {Hudaiberdiev, Sanjarbek and Ovcharenko, Ivan}, journal = {eLife (in submission)}, year = {2024}, google_scholar_id = {0EnyYjriUFMC}, url = {https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2023.02.05.527203v3.abstract} }
2023
-
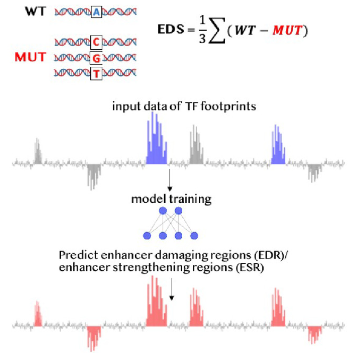 Modeling islet enhancers using deep learning identifies candidate causal variants at loci associated with T2D and glycemic traitsSanjarbek Hudaiberdiev, D Leland Taylor , Wei Song , and 8 more authorsProceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2023
Modeling islet enhancers using deep learning identifies candidate causal variants at loci associated with T2D and glycemic traitsSanjarbek Hudaiberdiev, D Leland Taylor , Wei Song , and 8 more authorsProceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2023Genetic association studies have identified hundreds of independent signals associated with type 2 diabetes (T2D) and related traits. Despite these successes, the identification of specific causal variants underlying a genetic association signal remains challenging. In this study, we describe a deep learning (DL) method to analyze the impact of sequence variants on enhancers. Focusing on pancreatic islets, a T2D relevant tissue, we show that our model learns islet-specific transcription factor (TF) regulatory patterns and can be used to prioritize candidate causal variants. At 101 genetic signals associated with T2D and related glycemic traits where multiple variants occur in linkage disequilibrium, our method nominates a single causal variant for each association signal, including three variants previously shown to alter reporter activity in islet-relevant cell types. For another signal associated with blood glucose levels, we biochemically test all candidate causal variants from statistical fine-mapping using a pancreatic islet beta cell line and show biochemical evidence of allelic effects on TF binding for the model-prioritized variant. To aid in future research, we publicly distribute our model and islet enhancer perturbation scores across 67 million genetic variants. We anticipate that DL methods like the one presented in this study will enhance the prioritization of candidate causal variants for functional studies.
@article{hudaiberdiev2023modeling, title = {Modeling islet enhancers using deep learning identifies candidate causal variants at loci associated with T2D and glycemic traits}, author = {Hudaiberdiev, Sanjarbek and Taylor, D Leland and Song, Wei and Narisu, Narisu and Bhuiyan, Redwan M and Taylor, Henry J and Tang, Xuming and Yan, Tingfen and Swift, Amy J and Bonnycastle, Lori L and others}, journal = {Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences}, volume = {120}, number = {35}, pages = {e2206612120}, year = {2023}, google_scholar_id = {Se3iqnhoufwC}, url = {https://www.pnas.org/doi/full/10.1073/pnas.2206612120?doi=10.1073/pnas.2206612120} } -
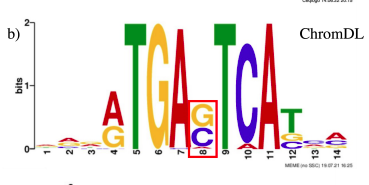 ChromDL: A Next-Generation Regulatory DNA ClassifierChristopher Hill , Sanjarbek Hudaiberdiev, and Ivan OvcharenkoBioinformatics, 2023
ChromDL: A Next-Generation Regulatory DNA ClassifierChristopher Hill , Sanjarbek Hudaiberdiev, and Ivan OvcharenkoBioinformatics, 2023Predicting the regulatory function of non-coding DNA using only the DNA sequence continues to be a major challenge in genomics. With the advent of improved optimization algorithms, faster GPU speeds, and more intricate machine learning libraries, hybrid convolutional and recurrent neural network architectures can be constructed and applied to extract crucial information from non-coding DNA. Using a comparative analysis of the performance of thousands of Deep Learning (DL) architectures, we developed ChromDL, a neural network architecture combining bidirectional gated recurrent units (BiGRU), convolutional neural networks (CNNs), and bidirectional long short-term memory units (BiLSTM), which significantly improves upon a range of prediction metrics compared to its predecessors in transcription factor binding site (TFBS), histone modification (HM), and DNase-I hypersensitive site (DHS) detection. Combined with a secondary model, it can be utilized for accurate classification of gene regulatory elements. The model can also detect weak transcription factor (TF) binding with higher accuracy as compared to previously developed methods and has the potential to accurately delineate TF binding motif specificities.
@article{hill2023chromdl, title = {ChromDL: A Next-Generation Regulatory DNA Classifier}, author = {Hill, Christopher and Hudaiberdiev, Sanjarbek and Ovcharenko, Ivan}, journal = {Bioinformatics}, pages = {2023--01}, year = {2023}, doi = {10.1101/2023.01.27.525971}, google_scholar_id = {UebtZRa9Y70C}, url = {https://academic.oup.com/bioinformatics/article/39/Supplement_1/i377/7210509} } - Sequence characteristics and an accurate model of abundant hyperactive loci in the human genomeSanjarbek Hudaiberdiev, and Ivan OvcharenkobioRxiv: the preprint server for biology, 2023
Enhancers and promoters are classically considered to be bound by a small set of TFs in a sequence-specific manner. This assumption has come under increasing skepticism as the datasets of ChIP-seq assays of TFs have expanded. In particular, high-occupancy target (HOT) loci attract hundreds of TFs with seemingly no detectable correlation between ChIP-seq peaks and DNA-binding motif presence. Here, we used a set of 1,003 TF ChIP-seq datasets (HepG2, K562, H1) to analyze the patterns of ChIP-seq peak co-occurrence in combination with functional genomics datasets. We identified 43,891 HOT loci forming at the promoter (53%) and enhancer (47%) regions. HOT promoters regulate housekeeping genes, whereas HOT enhancers are involved in tissue-specific process regulation. HOT loci form the foundation of human super-enhancers and evolve under strong negative selection, with some of these loci being located in ultraconserved regions. Sequence-based classification analysis of HOT loci suggested that their formation is driven by the sequence features, and the density of mapped ChIP-seq peaks across TF-bound loci correlates with sequence features and the expression level of flanking genes. Based on the affinities to bind to promoters and enhancers we detected 5 distinct clusters of TFs that form the core of the HOT loci. We report an abundance of HOT loci in the human genome and a commitment of 51% of all TF ChIP-seq binding events to HOT locus formation thus challenging the classical model of enhancer activity and propose a model of HOT locus formation based on the existence of large transcriptional condensates.
@article{hudaiberdiev2023sequencf, title = {Sequence characteristics and an accurate model of abundant hyperactive loci in the human genome}, author = {Hudaiberdiev, Sanjarbek and Ovcharenko, Ivan}, journal = {bioRxiv: the preprint server for biology}, year = {2023}, google_scholar_id = {0EnyYjriUFMC}, url = {https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2023.02.05.527203.abstract} }
2020
-
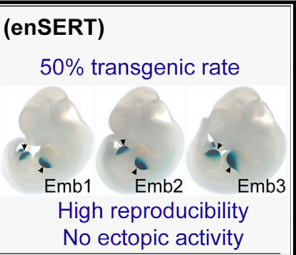 Comprehensive in vivo interrogation reveals phenotypic impact of human enhancer variantsEvgeny Z Kvon , Yiwen Zhu , Guy Kelman , and 8 more authorsCell, 2020
Comprehensive in vivo interrogation reveals phenotypic impact of human enhancer variantsEvgeny Z Kvon , Yiwen Zhu , Guy Kelman , and 8 more authorsCell, 2020Establishing causal links between non-coding variants and human phenotypes is an increasing challenge. Here, we introduce a high-throughput mouse reporter assay for assessing the pathogenic potential of human enhancer variants in vivo and examine nearly a thousand variants in an enhancer repeatedly linked to polydactyly. We show that 71% of all rare non-coding variants previously proposed as causal lead to reporter gene expression in a pattern consistent with their pathogenic role. Variants observed to alter enhancer activity were further confirmed to cause polydactyly in knockin mice. We also used combinatorial and single-nucleotide mutagenesis to evaluate the in vivo impact of mutations affecting all positions of the enhancer and identified additional functional substitutions, including potentially pathogenic variants hitherto not observed in humans. Our results uncover the functional consequences of hundreds of mutations in a phenotype-associated enhancer and establish a widely applicable strategy for systematic in vivo evaluation of human enhancer variants.
@article{kvon2020comprehensive, title = {Comprehensive in vivo interrogation reveals phenotypic impact of human enhancer variants}, author = {Kvon, Evgeny Z and Zhu, Yiwen and Kelman, Guy and Novak, Catherine S and Plajzer-Frick, Ingrid and Kato, Momoe and Garvin, Tyler H and Pham, Quan and Harrington, Anne N and Hunter, Riana D and others}, journal = {Cell}, volume = {180}, number = {6}, pages = {1262--1271}, year = {2020}, publisher = {Elsevier}, google_scholar_id = {WF5omc3nYNoC}, url = {https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0092867420302087} }
2017
-
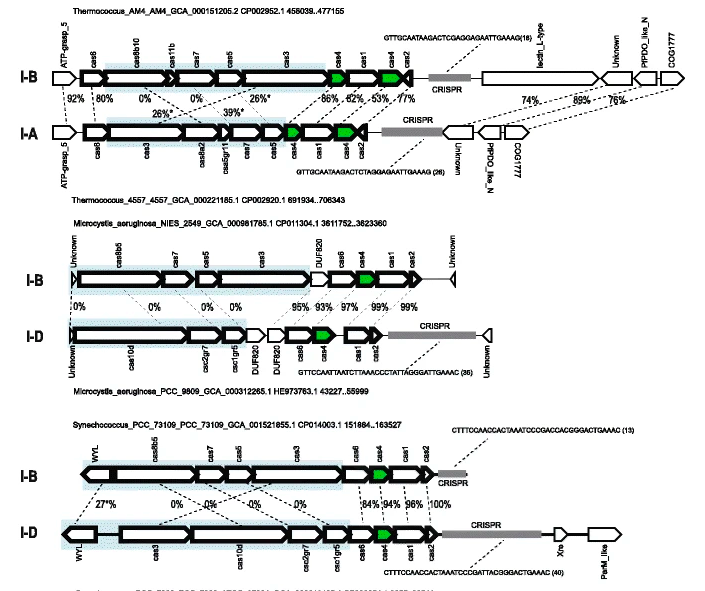 Phylogenomics of Cas4 family nucleasesSanjarbek Hudaiberdiev, Sergey Shmakov , Yuri I Wolf , and 3 more authorsBMC evolutionary biology, 2017
Phylogenomics of Cas4 family nucleasesSanjarbek Hudaiberdiev, Sergey Shmakov , Yuri I Wolf , and 3 more authorsBMC evolutionary biology, 2017The Cas4 family endonuclease is a component of the adaptation module in many variants of CRISPR-Cas adaptive immunity systems. Unlike most of the other Cas proteins, Cas4 is often encoded outside CRISPR-cas loci (solo-Cas4) and is also found in mobile genetic elements (MGE-Cas4). As part of our ongoing investigation of CRISPR-Cas evolution, we explored the phylogenomics of the Cas4 family. About 90% of the archaeal genomes encode Cas4 compared to only about 20% of the bacterial genomes. Many archaea encode both the CRISPR-associated form (CAS-Cas4) and solo-Cas4, whereas in bacteria, this combination is extremely rare. The solo-cas4 genes are over-represented in environmental bacteria and archaea with small genomes that typically lack CRISPR-Cas, suggesting that Cas4 could perform uncharacterized defense or repair functions in these microbes. Phylogenomic analysis indicates that both the CRISPR-associated cas4 genes are often transferred horizontally but almost exclusively, as part of the adaptation module. The evolutionary integrity of the adaptation module sharply contrasts the rampant shuffling of CRISPR-cas modules whereby a given variant of the adaptation module can combine with virtually any effector module. The solo-cas4 genes evolve primarily via vertical inheritance and are subject only to occasional horizontal transfer. The selection pressure on cas4 genes does not substantially differ between CAS-Cas4 and solo-cas4, and is close to the genomic median. Thus, cas4 genes, similarly to cas1 and cas2, evolve similarly to ‘regular’ microbial genes involved in various cellular functions, showing no evidence of direct involvement in virus-host arms races. A notable feature of the Cas4 family evolution is the frequent recruitment of cas4 genes by various mobile genetic elements (MGE), particularly, archaeal viruses. The functions of Cas4 in these elements are unknown and potentially might involve anti-defense roles. Unlike most of the other Cas proteins, Cas4 family members are as often encoded by stand-alone genes as they are incorporated in CRISPR-Cas systems. In addition, cas4 genes were repeatedly recruited by MGE, perhaps, for anti-defense functions. Experimental characterization of the solo and MGE-encoded Cas4 nucleases is expected to reveal currently uncharacterized defense and anti-defense systems and their interactions with CRISPR-Cas systems.
@article{hudaiberdiev2017phylogenomics, title = {Phylogenomics of Cas4 family nucleases}, author = {Hudaiberdiev, Sanjarbek and Shmakov, Sergey and Wolf, Yuri I and Terns, Michael P and Makarova, Kira S and Koonin, Eugene V}, journal = {BMC evolutionary biology}, volume = {17}, number = {1}, pages = {1--14}, year = {2017}, publisher = {BioMed Central}, google_scholar_id = {Y0pCki6q_DkC}, url = {https://bmcecolevol.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12862-017-1081-1} }
2015
-
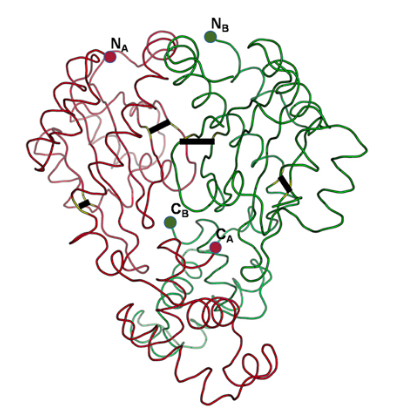 Census of solo LuxR genes in prokaryotic genomesSanjarbek Hudaiberdiev, Kumari S Choudhary , Roberto Vera Alvarez , and 4 more authorsFrontiers in cellular and infection microbiology, 2015
Census of solo LuxR genes in prokaryotic genomesSanjarbek Hudaiberdiev, Kumari S Choudhary , Roberto Vera Alvarez , and 4 more authorsFrontiers in cellular and infection microbiology, 2015luxR genes encode transcriptional regulators that control acyl homoserine lactone-based quorum sensing (AHL QS) in Gram negative bacteria. On the bacterial chromosome, luxR genes are usually found next or near to a luxI gene encoding the AHL signal synthase. Recently, a number of luxR genes were described that have no luxI genes in their vicinity on the chromosome. These so-called solo luxR genes may either respond to internal AHL signals produced by a non-adjacent luxI in the chromosome, or can respond to exogenous signals. Here we present a survey of solo luxR genes found in complete and draft bacterial genomes in the NCBI databases using HMMs. We found that 2698 of the 3550 luxR genes found are solos, which is an unexpectedly high number even if some of the hits may be false positives. We also found that solo LuxR sequences form distinct clusters that are different from the clusters of LuxR sequences that are part of the known luxR-luxI topological arrangements. We also found a number of cases that we termed twin luxR topologies, in which two adjacent luxR genes were in tandem or divergent orientation. Many of the luxR solo clusters were devoid of the sequence motifs characteristic of AHL binding LuxR proteins so there is room to speculate that the solos may be involved in sensing hitherto unknown signals. It was noted that only some of the LuxR clades are rich in conserved cysteine residues. Molecular modeling suggests that some of the cysteines may be involved in disulfide formation, which makes us speculate that some LuxR proteins, including some of the solos may be involved in redox regulation.
@article{hudaiberdiev2015census, title = {Census of solo LuxR genes in prokaryotic genomes}, author = {Hudaiberdiev, Sanjarbek and Choudhary, Kumari S and Vera Alvarez, Roberto and Gelencs{\'e}r, Zsolt and Ligeti, Bal{\'a}zs and Lamba, Doriano and Pongor, S{\'a}ndor}, journal = {Frontiers in cellular and infection microbiology}, volume = {5}, pages = {20}, year = {2015}, publisher = {Frontiers Media SA}, google_scholar_id = {2osOgNQ5qMEC}, url = {https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcimb.2015.00020/full} }
2014
-
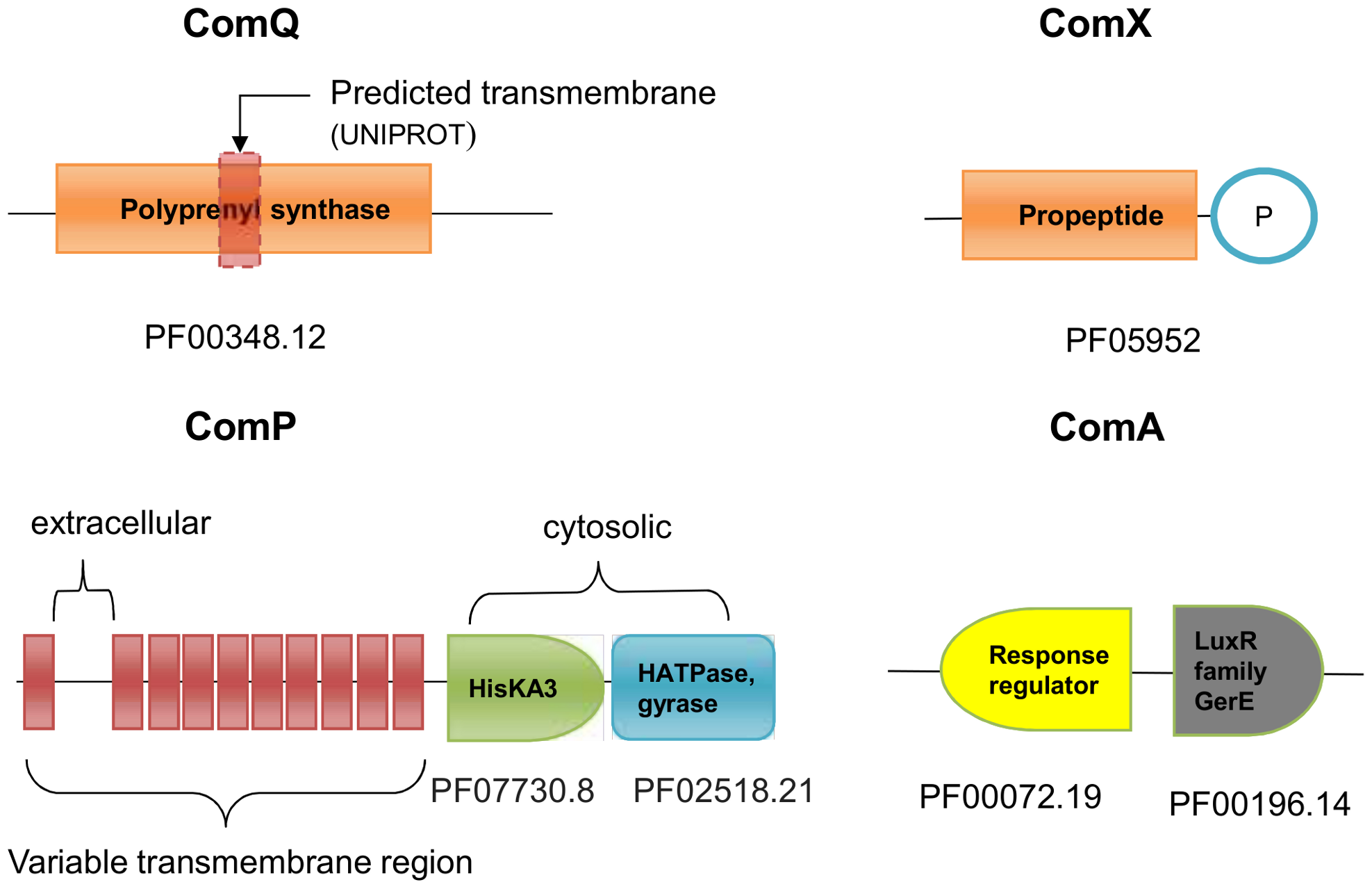 ComQXPA quorum sensing systems may not be unique to Bacillus subtilis: a census in prokaryotic genomesIztok Dogsa , Kumari Sonal Choudhary , Ziva Marsetic , and 4 more authorsPloS one, 2014
ComQXPA quorum sensing systems may not be unique to Bacillus subtilis: a census in prokaryotic genomesIztok Dogsa , Kumari Sonal Choudhary , Ziva Marsetic , and 4 more authorsPloS one, 2014The comQXPA locus of Bacillus subtilis encodes a quorum sensing (QS) system typical of Gram positive bacteria. It encodes four proteins, the ComQ isoprenyl transferase, the ComX pre-peptide signal, the ComP histidine kinase, and the ComA response regulator. These are encoded by four adjacent genes all situated on the same chromosome strand. Here we present results of a comprehensive census of comQXPA-like gene arrangements in 2620 complete and 6970 draft prokaryotic genomes (sequenced by the end of 2013). After manually checking the data for false-positive and false-negative hits, we found 39 novel com-like predictions. The census data show that in addition to B. subtilis and close relatives, 20 comQXPA-like loci are predicted to occur outside the B. subtilis clade. These include some species of Clostridiales order, but none outside the phylum Firmicutes. Characteristic gene-overlap patterns were observed in comQXPA loci, which were different for the B. subtilis-like and non-B. subtilis-like clades. Pronounced sequence variability associated with the ComX peptide in B. subtilis clade is evident also in the non-B. subtilis clade suggesting grossly similar evolutionary constraints in the underlying quorum sensing systems.
@article{dogsa2014comqxpa, title = {ComQXPA quorum sensing systems may not be unique to Bacillus subtilis: a census in prokaryotic genomes}, author = {Dogsa, Iztok and Choudhary, Kumari Sonal and Marsetic, Ziva and Hudaiberdiev, Sanjarbek and Vera, Roberto and Pongor, S{\'a}ndor and Mandic-Mulec, Ines}, journal = {PloS one}, volume = {9}, number = {5}, pages = {e96122}, year = {2014}, publisher = {Public Library of Science San Francisco, USA}, google_scholar_id = {d1gkVwhDpl0C}, url = {https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0096122} }
2013
-
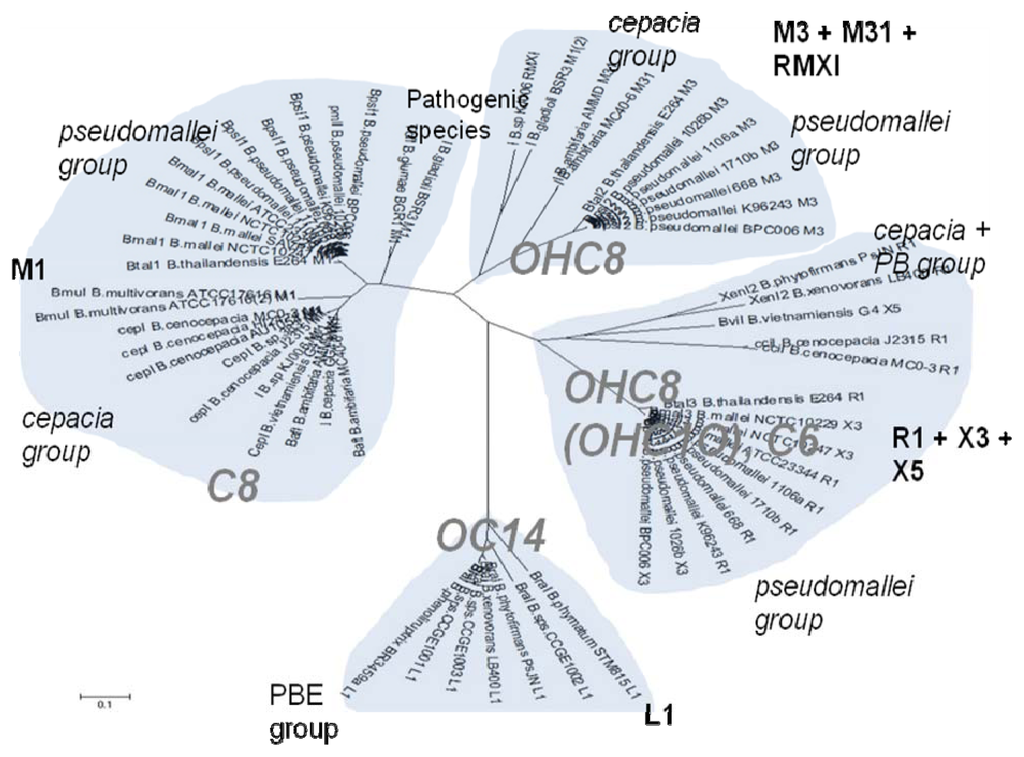 The organization of the quorum sensing luxI/R family genes in BurkholderiaKumari Sonal Choudhary , Sanjarbek Hudaiberdiev, Zsolt Gelencsér , and 3 more authorsInternational journal of molecular sciences, 2013
The organization of the quorum sensing luxI/R family genes in BurkholderiaKumari Sonal Choudhary , Sanjarbek Hudaiberdiev, Zsolt Gelencsér , and 3 more authorsInternational journal of molecular sciences, 2013Members of the Burkholderia genus of Proteobacteria are capable of living freely in the environment and can also colonize human, animal and plant hosts. Certain members are considered to be clinically important from both medical and veterinary perspectives and furthermore may be important modulators of the rhizosphere. Quorum sensing via N-acyl homoserine lactone signals (AHL QS) is present in almost all Burkholderia species and is thought to play important roles in lifestyle changes such as colonization and niche invasion. Here we present a census of AHL QS genes retrieved from public databases and indicate that the local arrangement (topology) of QS genes, their location within chromosomes and their gene neighborhoods show characteristic patterns that differ between the known Burkholderia clades. In sequence phylogenies, AHL QS genes seem to cluster according to the local gene topology rather than according to the species, which suggests that the basic topology types were present prior to the appearance of current Burkholderia species. The data are available at http://net.icgeb.org/burkholderia/.
@article{choudhary2013organization, title = {The organization of the quorum sensing luxI/R family genes in Burkholderia}, author = {Choudhary, Kumari Sonal and Hudaiberdiev, Sanjarbek and Gelencs{\'e}r, Zsolt and Coutinho, Bruna Gon{\c{c}}alves and Venturi, Vittorio and Pongor, S{\'a}ndor}, journal = {International journal of molecular sciences}, volume = {14}, number = {7}, pages = {13727--13747}, year = {2013}, publisher = {Molecular Diversity Preservation International (MDPI)}, google_scholar_id = {u5HHmVD_uO8C}, url = {https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/14/7/13727} } - The Organization of the Quorum Sensing luxI/R Family Genes in BurkholderiaSándor Pongor , Vittorio Venturi , Bruna Gonçalves Coutinho , and 3 more authors2013
@article{pongor2013organization, title = {The Organization of the Quorum Sensing luxI/R Family Genes in Burkholderia}, author = {Pongor, S{\'a}ndor and Venturi, Vittorio and Coutinho, Bruna Gon{\c{c}}alves and Gelencs{\'e}r, Zsolt and Choudhary, Kumari Sonal and Hudaiberdiev, Sanjarbek}, year = {2013}, google_scholar_id = {u5HHmVD_uO8C}, url = {https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/14/7/13727} }
2012
-
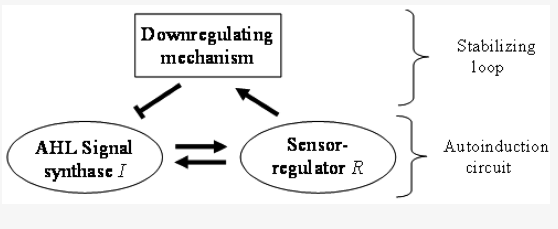 Classifying the topology of AHL-driven quorum sensing circuits in proteobacterial genomesZsolt Gelencsér , Kumari Sonal Choudhary , Bruna Goncalves Coutinho , and 4 more authorsSensors, 2012
Classifying the topology of AHL-driven quorum sensing circuits in proteobacterial genomesZsolt Gelencsér , Kumari Sonal Choudhary , Bruna Goncalves Coutinho , and 4 more authorsSensors, 2012Virulence and adaptability of many Gram-negative bacterial species are associated with an N-acylhomoserine lactone (AHL) gene regulation mechanism called quorum sensing (QS). The arrangement of quorum sensing genes is variable throughout bacterial genomes, although there are unifying themes that are common among the various topological arrangements. A bioinformatics survey of 1,403 complete bacterial genomes revealed characteristic gene topologies in 152 genomes that could be classified into 16 topological groups. We developed a concise notation for the patterns and show that the sequences of LuxR regulators and LuxI autoinducer synthase proteins cluster according to the topological patterns. The annotated topologies are deposited online with links to sequences and genome annotations at http://bacteria.itk.ppke.hu/QStopologies/.
@article{gelencser2012classifying, title = {Classifying the topology of AHL-driven quorum sensing circuits in proteobacterial genomes}, author = {Gelencs{\'e}r, Zsolt and Choudhary, Kumari Sonal and Coutinho, Bruna Goncalves and Hudaiberdiev, Sanjarbek and Galb{\'a}ts, Borisz and Venturi, Vittorio and Pongor, S{\'a}ndor}, journal = {Sensors}, volume = {12}, number = {5}, pages = {5432--5444}, year = {2012}, publisher = {Molecular Diversity Preservation International (MDPI)}, google_scholar_id = {u-x6o8ySG0sC}, url = {https://www.mdpi.com/1424-8220/12/5/5432} } -
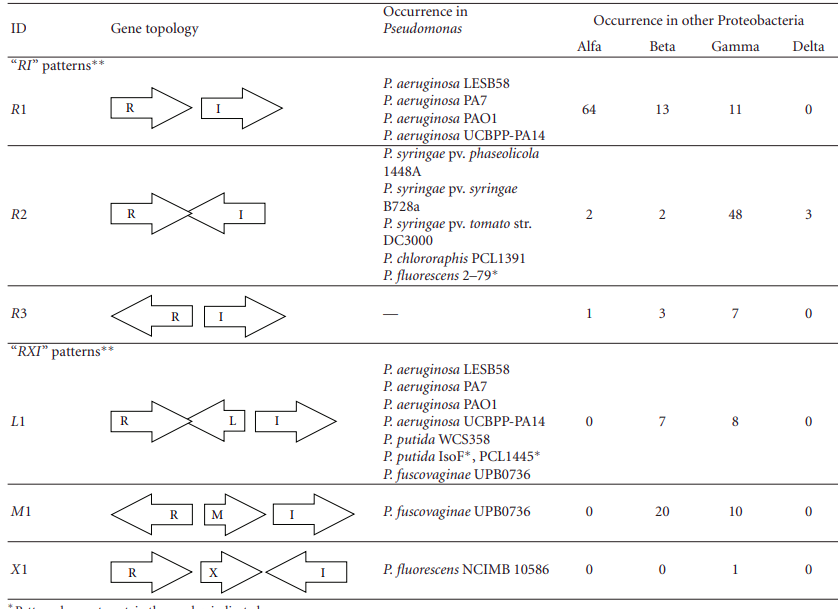 Chromosomal arrangement of AHL-driven quorum sensing circuits in PseudomonasZsolt Gelencsér , Borisz Galbáts , Juan F Gonzalez , and 4 more authorsInternational Scholarly Research Notices, 2012
Chromosomal arrangement of AHL-driven quorum sensing circuits in PseudomonasZsolt Gelencsér , Borisz Galbáts , Juan F Gonzalez , and 4 more authorsInternational Scholarly Research Notices, 2012Pseudomonas spp. are able to colonize a large variety of environments due to their wide adaptability which is also associated with an N-acyl homoserine lactone (AHL) gene regulation mechanism called quorum sensing (QS). In this article we present a systematic overview of the genomic arrangement patterns of quorum sensing genes found in Pseudomonas and compare the topologies with those found in other bacterial genomes. We find that the topological arrangement of QS genes is more variable than previously thought but there are a few unifying features that occur in many of the topological arrangements. We hypothesize that the negative regulators of QS that are often found between the canonical luxR/ and luxI-family genes may be crucial for stabilizing the output of QS circuits.
@article{gelencser2012chromosomal, title = {Chromosomal arrangement of AHL-driven quorum sensing circuits in Pseudomonas}, author = {Gelencs{\'e}r, Zsolt and Galb{\'a}ts, Borisz and Gonzalez, Juan F and Choudhary, K Sonal and Hudaiberdiev, Sanjarbek and Venturi, Vittorio and Pongor, S{\'a}ndor}, journal = {International Scholarly Research Notices}, volume = {2012}, year = {2012}, publisher = {Hindawi}, google_scholar_id = {9yKSN-GCB0IC}, url = {https://downloads.hindawi.com/archive/2012/484176.pdf} } - Chromosomal Arrangement of AHL-Driven Quorum Sensing Circuits in PseudomonasSanjarbek Hudaiberdiev, Vittorio Venturi , and S Pongor2012
Pseudomonas spp. are able to colonize a large variety of environments due to their wide adaptability which is also associated with an N-acyl homoserine lactone (AHL) gene regulation mechanism called quorum sensing (QS). In this article we present a systematic overview of the genomic arrangement patterns of quorum sensing genes found in Pseudomonas and compare the topologies with those found in other bacterial genomes. We find that the topological arrangement of QS genes is more variable than previously thought but there are a few unifying features that occur in many of the topological arrangements. We hypothesize that the negative regulators of QS that are often found between the canonical luxR/ and luxI-family genes may be crucial for stabilizing the output of QS circuits.
@article{hudaiberdiev2012chromosomal, title = {Chromosomal Arrangement of AHL-Driven Quorum Sensing Circuits in Pseudomonas}, author = {Hudaiberdiev, Sanjarbek and Venturi, Vittorio and {\'a}ndor Pongor, S}, year = {2012}, google_scholar_id = {9yKSN-GCB0IC}, url = {https://downloads.hindawi.com/archive/2012/484176.pdf} }







